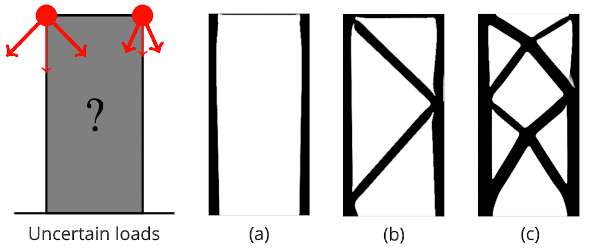Electrodynamics:
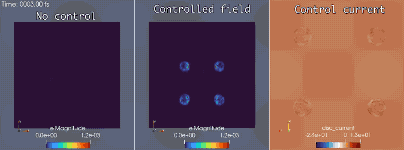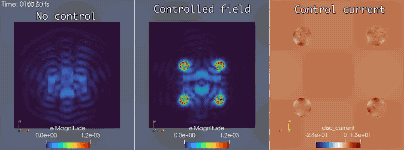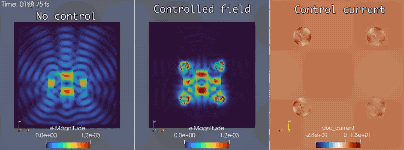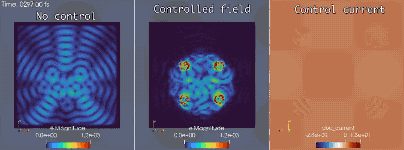
Extreme-scale optimal control for electronic camouflage
In conjunction with the Mirage electromagnetics module of the extreme-scale simulator MrHyDE, ROL computes an optimal control strategy to mask a source of electromagnetic waves.
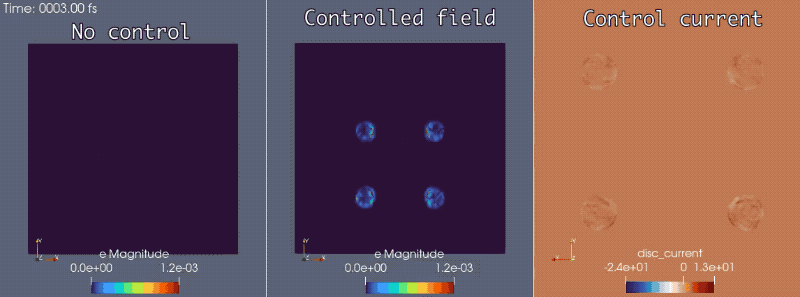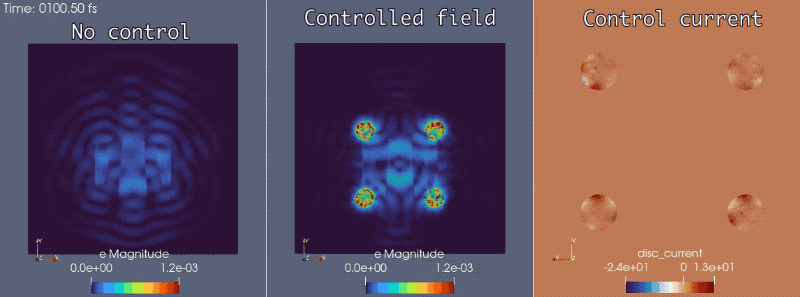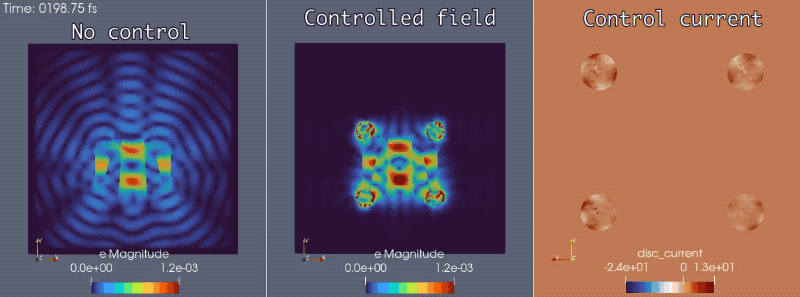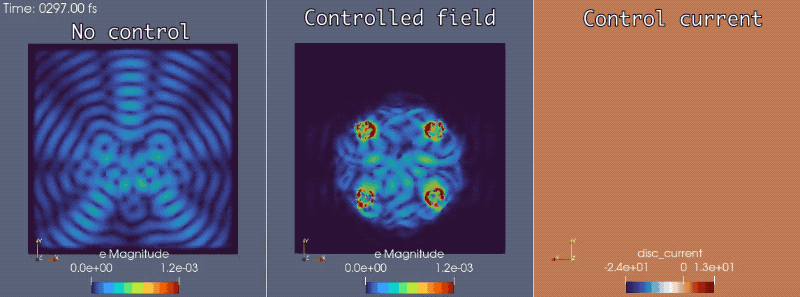
Fluid dynamics:
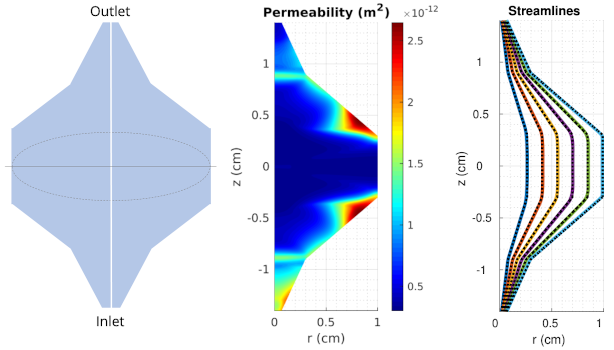
Optimization enables new additive manufacturing applications
Using the Darcy module of its PDE-constrained optimization test suite PDE-OPT, ROL designs porous media in columns used by chemical engineers, to enforce uniform transit time of the fluid between an inlet and an outlet.
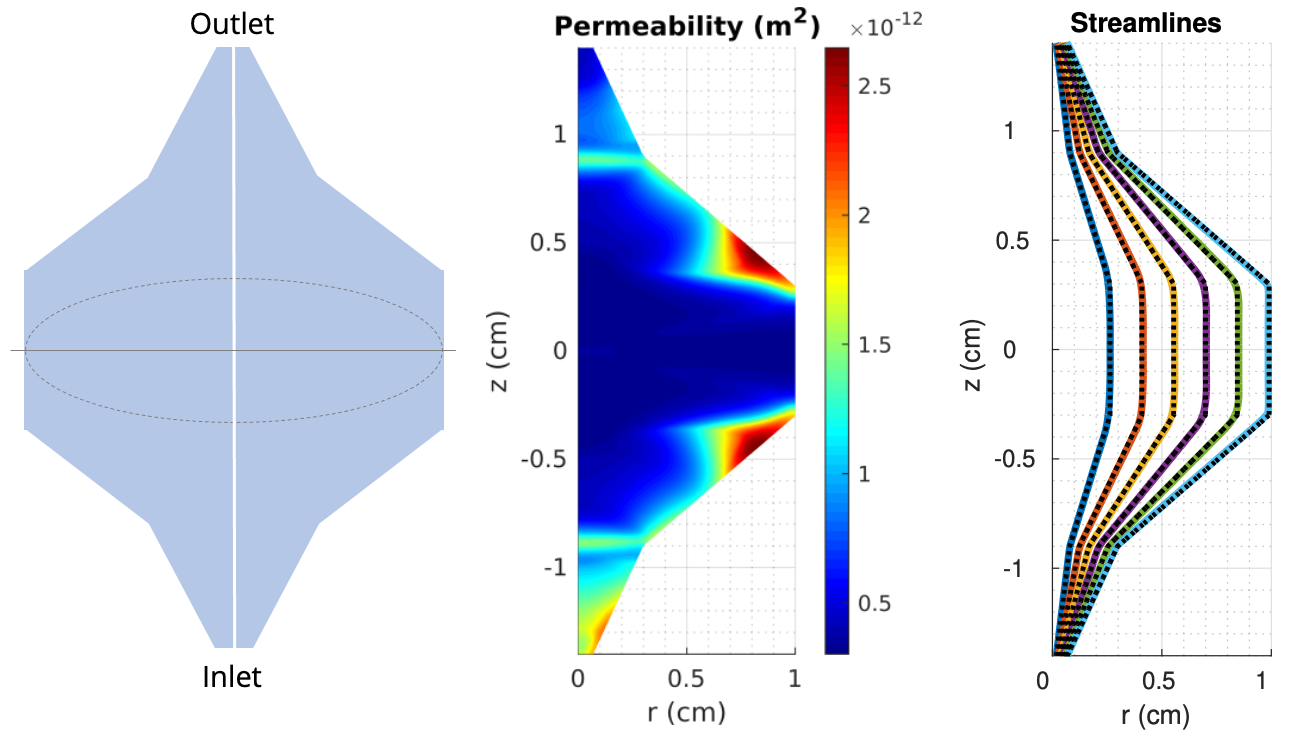
H. Antil, D. P. Kouri, D. Ridzal, D. B. Robinson, M. Salloum (2023) Uniform flow in axisymmetric devices through permeability optimization, submitted.
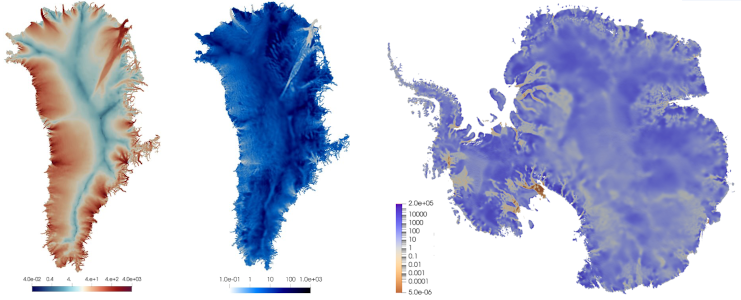
Climate science:
Computing basal friction to accurately predict flow of land ice
Coupled with the ice-sheet model MALI (MPAS Albany Land Ice), ROL is used to estimate the basal friction coefficients of Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets, based on ice velocity observations.
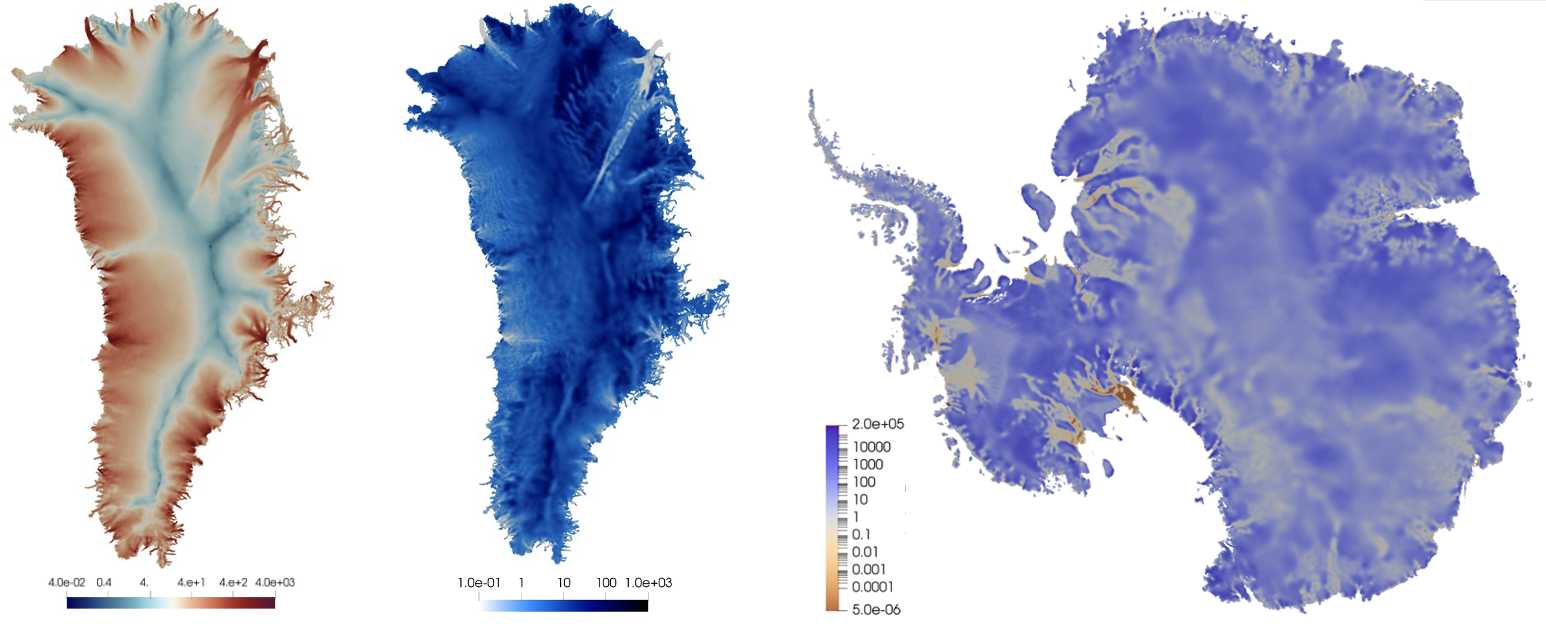
M. Perego (2022) Large-scale PDE-constrained Optimization for Ice Sheet Model Initialization, SIAM News.
Structural dynamics:
Stochastic optimization reduces risk of structural failure
Using the elasticity module of its PDE-constrained optimization test suite PDE-OPT, ROL computes risk-averse designs of structures subject to random loads. Here, we use the conditional value-at-risk (CVaR) to generate structures that are less likely to fail.
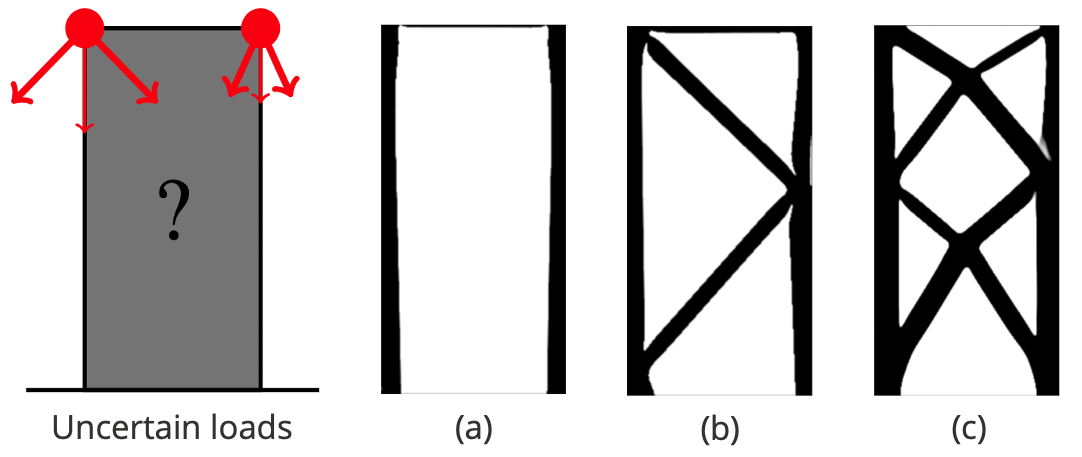
Image processing:
New algorithms for enhanced super-resolution on GPUs
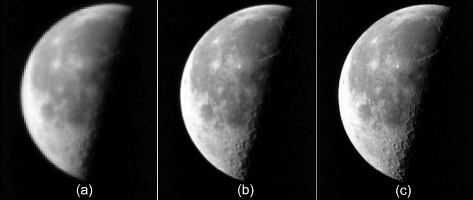
Coupled with the GPU-accelerated image processing routines from ArrayFire, ROL is used for super-resolution imaging, to recover a high-resolution image from a sequence of low-resolution images resulting from lateral jitter.
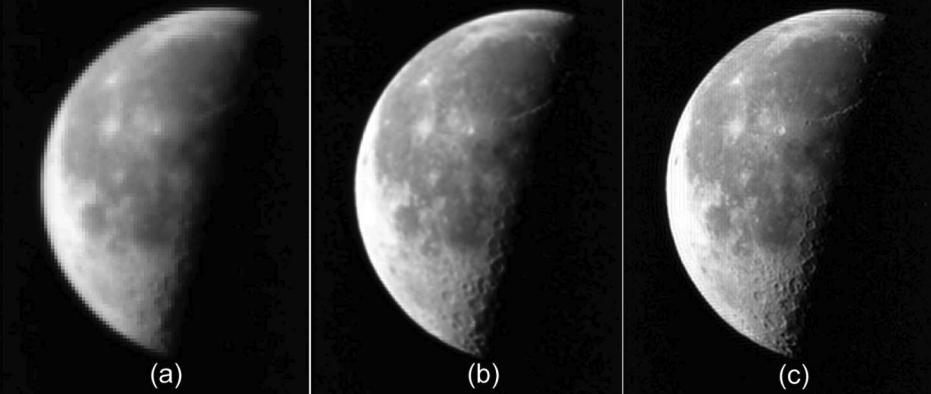
D.P. Kouri, E.A. Shields (2014) Efficient multiframe super-resolution for imagery with lateral shifts, Applied Optics 53(24), F1-F9.
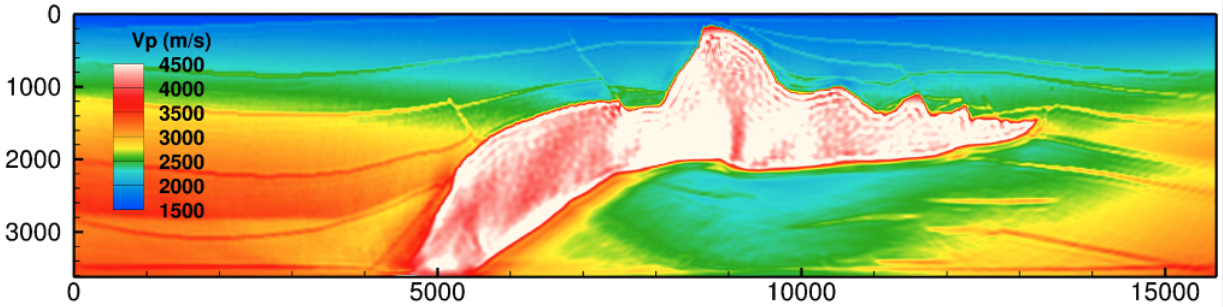
Geophysics:
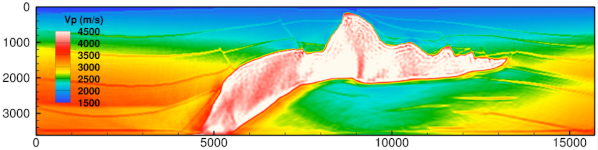
Exploring Earth’s subsurface through full-waveform seismic inversion
Using Sandia’s discontinuous Galerkin finite element simulator DGM, ROL is used for full-waveform seismic inversion.